SVM-based Classification Framework
Associating Images with High-Level Semantic Concepts
The SVM-based classification framework, which came up as a result of ITI's research activity on the knowledge-assisted multimedia analysis research field, supports the automatic image segmentation and semantic annotation at region level. Semantic annotation concerns the association of every image region with pre-defined high-level semantic concepts.
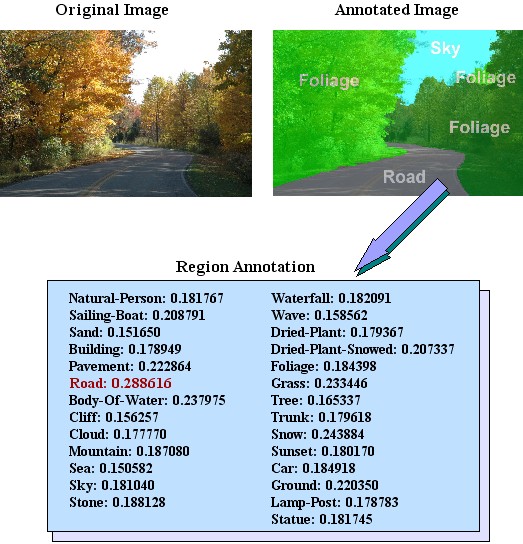
The examined image is initially segmented, using the algorithm proposed in [1], and the following MPEG-7 descriptors are extracted for every resulting region: Scalable Colour, Region Shape, Homogeneous Texture and Edge Histogram.
The core functionality of the developed framework consists of a Support Vector Machines (SVMs) structure. Specifically, an individual SVM is introduced for every defined high-level concept to detect the corresponding instances based on the calculated low-level descriptors. Each SVM is trained under the ‘one-against-all' approach.
In the current stage of development, 27 high-level semantic concepts are supported: Natural-Person, Sailing-Boat, Sand, Building, Pavement, Road, Body-Of-Water, Cliff, Cloud, Mountain, Sea, Sky, Stone, Waterfall, Wave, Dried-Plant, Dried-Plant-Snowed, Foliage, Grass, Tree, Trunk, Snow, Sunset, Car, Ground, Lamp-Post, Statue.
Download an executable version of the developed classification framework.
An extension of the provided software, namely an ontology-based unified framework for realizing semantic image analysis and classification, has also been developed and is described in [2].
[1] V. Mezaris, I. Kompatsiaris and M. G. Strintzis, "Still Image Segmentation Tools for Object-based Multimedia Applications", International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 701-725, June 2004.
[2] G. Th. Papadopoulos, V. Mezaris, I. Kompatsiaris and M. G. Strintzis: "Combining Global and Local Information for Knowledge-Assisted Image Analysis and Classification", EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, Special Issue on Knowledge-Assisted Media Analysis for Interactive Multimedia Applications, , vol. 2007 (2007), Article ID 45842.
