LUMO
The LinkedTV User Model Ontology (LUMO)
LUMO [owl]
LUMO_mappings [owl]
LUMO documentation [html]
LUMO mappings documentation [html]
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License (version 3.0). This copyright applies to the LUMO Ontology, the LUMO mappings ontology and accompanying documentation.
Creator and publisher: CERTH-ITI
Influence by existing vocabularies
Mappings to existing vocabularies
Summary
The LUMO ontology is developed within the LinkedTV project to semantically represent user-pertinent information, in order to enable semantic personalization and contextualization (i.e. filtering) of concepts and content in the networked media domain. LUMO is designed as an OWL ontology, with its expressivity restricted to the OWL 2 RL profile, in order to maintain the minimal complexity as per the LinkedTV requirements and address scalability and user privacy issues. LUMO is currently accompanied by a separate mappings ontology, modeling mappings of LUMO to several existing ontologies and vocabularies.
LUMO is published under the http://data.linkedtv.eu/ontologies/lumo namespace.
Status of this document
The LUMO ontology is currently under engineering. Updates are expected on the current version.
Overview
LUMO addresses four major user-pertinent aspects: Context Dimensions, Domain-dependent dimensions, Agents and Spatio-Temporal concepts. The two latter aspects may regard both contextual and domain-dependent aspects of the user and as so are modeled independently on the top of the hierarchy.
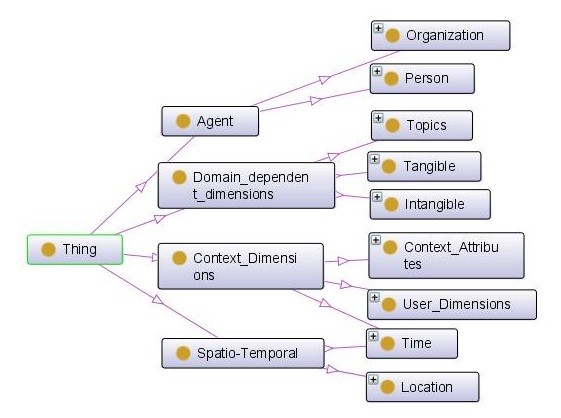
The LUMO top hierarchy
Apart from the taxonomy, LUMO models a number of universal restriction axioms relating concepts via non-taxonomical object properties. In the current version, such axioms are mostly of the type Type ⊑ ∀has(Sub)Topic.Topic and enable inference of topics in both the content’s annotation and in the user pro- file, since content annotation in LinkedTV does not provide this information. Type corresponds to the type of an entity in the annotation (usually an agent, event, location or object), Topic is subsumed by the Topics concept/category of LUMO and hasSubTopic, hasTopic are roles (object properties), for which it holds hasSubTopic ⊑ hasTopic.

An example of a relation of concept Political_Agent to the topic-concept Politics via the hasTopic relation
Influence by existing vocabularies
LUMO engineering aims to model the most relevant entities and semantics from open vocabularies and adapt them to the networked media domain and the needs of the LinkedTV users. This includes adopting, adding new and appropriately discarding domain-extraneous information from relevant established vocabularies, as well as redefining semantics, with respect to leveraging LOD inconsistencies and enhancing coherency and completeness of modeled semantics.
The major existing vocabularies that have inspired and guided the engineering of LUMO are:
GUMO has guided the design of the top level context and domain-dependent dimensions, while several GUMO contextual dimensions where adopted and adapted to LinkedTV’s platform requirements (including camera-based sensor related concepts). Similarly, some LUMO “Topics” have been modeled to a great extent according to the corresponding GUMO "Topics".
The IPTC news codes were the main influence towards modeling the LUMO “Topics” hierarchy. Most upper topic categories were adopted per se and subcategories and concepts related to them where revised and adapted to the topics hierarchy. For instance, several subcategories were created (w.r.t. to also Wikipedia categories), while concepts in IPTC that were semantically direct descendants (with the “is-a” relationship) of the “Tangible” and “Intangible” LUMO categories were moved to that sub-hierarchy and related to "Topics" with the "hasTopic" and "hasSubtopic" object properties.
Schema.org influenced the modeling of the “Agent”, “Location”, “Intangible” and “Tangible” categories. These categories where populated also in correspondence to the DBPedia schema and the NERD ontology; in a smaller extent they were influenced by several other open vocabularies. Modeling these aspects heavily relied on representing information stemming from content annotation within the LinkedTV platform (for more information, cf. http://www.linkedtv.eu/research/linking-video-to-web-content/).
Mappings to existing vocabularies
The current version of LUMO is accompanied by a separate mappings ontology that maps LUMO to existing vocabularies. Mappings were generated automatically via the LogMap tool and evaluated and revised manually.
Mappings are detached from the ontology in order to enable user modeling and inferencing (recommendation) to take place in the minimum representative concept space, with regard to scalability and user privacy safeguarding issues. Mappings thus serve a) for interpretation of content annotation and b) as the means to facilitate re-use of the ontology by the Semantic Web.
The LUMO mappings ontology is published under the http://data.linkedtv.eu/ontologies/lumo_mappings namespace.
Currently, mappings are available to the main vocabularies that influenced the engineering of LUMO:
- DBPedia schema (currently with v3.8)
- schema.org
- NERD ontology
- IPTC news codes (as categorized by the WebTLab)
- GUMO
Mappings to other open vocabularies are under consideration and engineering. A future extension of LUMO is planned where fuzzy mappings will be embedded in the annotation of the LUMO entities, along with their semantic similarity, via the “isDescribedBy” LUMO annotation property (cf. http://www.slideshare.net/linkedtv/linked-tv-d42user-profile-schema-and-profile-capturing).


Mappings of LUMO concepts Animals and Organization to LOD vocabularies
Contacts
For LUMO and LUMO mappings related issues, please contact dorothea [at] iti [dot] gr.
For LinkedTV related issues, please contact bmezaris [at] iti [dot] gr.
